plasma
PlasmaTact for Surface Energy Modification and Bonding on Aerospace Composites
Introduction
The aerospace sector is pushing towards sustainability and reduction in their carbon emissions, as a result, there is a demand for lighter and more fuel-efficient aircraft. ‘Light weighting’ can be achieved using fibre-reinforced composite materials to construct primary and secondary structures of an aircraft. Circa 50% of the mass of the Boeing 787 ‘Dreamliner’ is accounted for by composite materials. Advantages such as excellent fatigue life, corrosion resistance, and improved thermal and electrical properties coupled with the weight-saving capability make fibre-reinforced composite materials desirable to aircraft manufacturers.
![Usage of composites in Boeing 787 Dreamliner structure [22].](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320951033/figure/fig1/AS:631662626996225@1527611514245/Usage-of-composites-in-Boeing-787-Dreamliner-structure-22.png)
The most common surface treatments are techniques such as sanding or grit blasting that physically abrade the bond surface, increasing the surface roughness that aids in mechanical interlocking between the adhesive and the adherend. These preparation techniques produce dust, which is undesirable for bonding, so solvent cleaning is usually performed after sanding. Plasma treatments are gaining widespread application in the automotive and aerospace industry as they not only clean the surface, but also change the chemical composition and surface energy aiding in an improved bonded joint.
Plasma treatments are gaining widespread application in the automotive and aerospace industry as they not only clean the surface, but also change the chemical composition and surface energy aiding in an improved bonded joint.
PlasmaTact 50 Testing
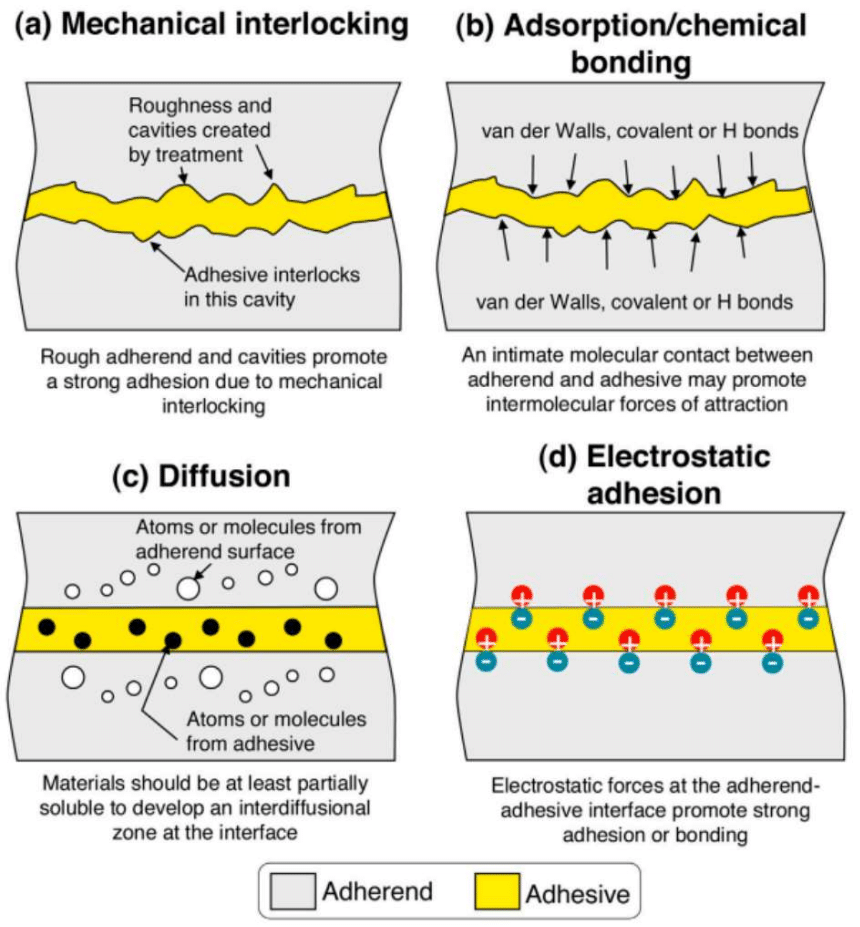
The main effects of plasma treatment on a composite surface are: modifying surface roughness due to the ablation effect; removal of contaminants; and, altering the surface chemistry. Hence, treatment of the composite adherends using plasma may activate both the mechanical interlocking and the chemical bonding adhesion mechanisms, maximising the adhesive bond strength. Concerning surface chemistry, research has found that it generally improves the oxygen content and creates polar components on the surface, which are essential for adhesive bonding [v]. Due to all these advantages,plasma treatment is gaining widespread applications in the aerospace and automotive sectors for use in adhesive bonding, with one of the most used plasma treatment systems being Atmospheric Pressure Plasma (APP) systems, due to their low operating costs and ease of use.
Surface Treatments
All composite samples were cleaned in an ultrasonic bath for 20 minutes before treatment. One set of samples was treated and characterised. For solvent cleaning, Isopropanol was used. For sanding, 240-grit sandpaper was used to abrade the surface in random directions; the grit size and sanding directions were chosen based on literature. The plasma torch parameters were set so that the optimal plasma was discharged for surface energy modification using pure argon gas: 50 W forward power, 0 W reflected power, 2.48 GHz frequency, 10 L/min gas flow rate, a 3 mm stand-off distance, and a processing speed of 1m/min.

Contact Angle (lower is better)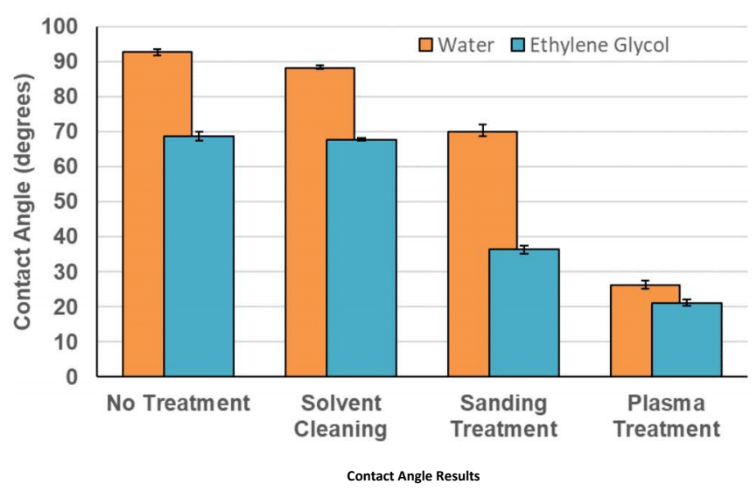
The non-treated sample has a hydrophobic surface, with a water contact angle of 92.1° and an ethylene glycol contact angle of 68.7°. Ethylene glycol contact angle will always be lower than water, on this material, as it has lesser surface tension. The solvent-cleaned sample has a marginally reduced contact angle; however, the sanding-treated samples have significantly reduced contact angles of 70.0°and 36.3° for water and ethylene glycol, respectively. Plasma treatment has a bigger reduction in contact angle: 26.1° and 21.1°, signifying a highly energised, hydrophilic surface.
Surface Energy (Higher is better)
The contact angles in Figure 10 were then used with the Wendt, Rabel and Kaelble method, to determine the surface energy of each composite sample. Figure above shows the results. The plasma
treated surface has the highest surface energy of 74.5mJ/m2, followed by the sanding-treated samples with a value of 37.1mJ/m2. The non-treated and solvent-cleaned samples have low surface energies of 20.7mJ/m2 and 22.0mJ/m2, respectively.
Surface Roughness (Lower is better)
The non-treated, solvent cleaned, and plasma treated samples have low roughness values of 0.16μm, 0.18μm, and 0.18μm, Ra, respectively. The sanding treatment has the highest Ra value of 0.64μm, because of the physical abrasion from the sandpaper.
Lap Shear Failure Load (Higher is better)
The average failure loads of the hybrid plasma treatment were lower than the plasma treated only specimens, which is an important outcome. Plasma treatment alone, was better than using any other treatment and better than using a hybrid approach with the next best treatment method.
Conclusion
The 50W Plasma Tact from Adtec Plasma improved the bonding strength of a carbon fibre composite. The plasma treatment may also be used, on it’s own, without the need for using traditional solvents or sand blasting techniques.
For more information regarding the PlasmaTact Series, click here.
Adtec PlasmaTact produces super hydrophilic surface on CSP glass at 30m/min
Adtec's new 50W PlasmaTact is capable of generating super hydrophilic surfaces on Concentrating Solar Power glass at speeds of 30 metres per minute, or half a metre per second, in just one pass of the material's surface.
A super hydrophilic surface is defined as one with a water contact angle of less than 5 degrees, and is a significant result for high-precision plasma torch processing.
In the context of CSP, producing a super hydrophilic surface means we could greatly reduce the water required for cleaning. Beyond this, creating such surfaces can greatly enhance our ability to bond materials.
The video below shows the 50W PlasmaTact, the latest development in Adtec's patented microwave induced argon plasma, processing the surface of the glass at 30m/minute. The image shows the resulting areas of super hydrophilicity - the water sticks preferentially to the treated regions.

Adtec launches 50W Cold Atmospheric Plasma Torch
Adtec first started to investigate cold atmospheric plasma back in 2005, as part of an anti-bacterial study in collaboration with the Max Planck Institute in Germany.
From here, we developed our patented coaxial microwave plasma technology, which remains at the core of our cold plasma products to this day.
As well as medical applications, Adtec developed PlasmaTact - a 15W torch for surface treatments and anti-bacterial applications.
We are now proud to announce the new, higher power 50W PlasmaTact. The increased power means that not only can we perform the same surface treatment tasks at higher speed, but a greater breadth of surface engineering applications become a possibility - keep an eye out for news on our upcoming work exploring etching and deposition at atmospheric pressure!
Adtec Healthcare's new project with Hull York Medical School testing gas plasma on Osteomyelitis bone infections.
We are excited to announce the study “Gas Plasma for the Prevention and Management of Osteomyelitis Biofilms” has now begun at the Hull York Medical School. The study led by Dr Angela Oates and funded by the National Biofilms Innovation Centre will seek to test the efficacy of our gas plasma system on osteomyelitis bone infections using our PlasmaTact device. This project will develop a novel laboratory testing model to evaluate and optimise plasma treatment for osteomyelitis biofilm infections.

We have already demonstrated that our gas plasma medical device, the Adtec SteriPlas, has proven antibacterial efficacy and accelerated healing in problematic and non-healing wounds with strong evidence collected from our extensive library of clinical trials and publications. This includes diabetic foot ulcers which are often complicated by biofilm. Over the course of its existence it has shown that no side effects have been reported which offers patients a safe and reliable treatment option. It has also shown that a 2-minute treatment time is sufficient to achieve exceptional results and that it is also a broad spectrum antibacterial with the ability to kill a wide range of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial superinfections.
The PlasmaTact utilizes the same gas plasma technology from the Adtec SteriPlas. The main difference between the two devices is that the PlasmaTact offers a smaller handheld style treatment area of 1cm2 (vs 12cm2 with the SteriPlas) and offers users the ability to change the power output settings (vs the fixed settings with the SteriPlas).
Osteomyelitis (OM) is biofilm infection of the bone and is a common and costly complication in diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) patients often resulting in amputations. Long-term antimicrobial therapy is widely used as a primary treatment for OM or as an adjunct to surgical approaches however, there is a failure rate of up to 35% and an associated increasing prevalence of antimicrobial resistance. There is an urgent clinical need to develop alternative non-antimicrobial approaches to treat infections, and currently there is a lack of credible alternatives in the market for the treatment of OM.
Evaluating the efficacy of gas plasma in OM represents unique challenges as both the biofilm growth and physical characteristics of OM bone will affect the delivery and activity of the plasma. In vitro biofilm model systems offer a means by which rapid, costs effective and standardised evaluation of anti-biofilm treatments can be undertaken.
The PATROL project is a new and exciting collaborative project between Adtec Healthcare and Dr Angela Oates of the University of Hull Wound Healing Group which is supported by NBIC PoC Award. The overall aim of this project is to develop an osteomyelitis biofilm infection model to support the optimisation and evaluation of a cold plasma technology for the management and prevention of OM.
This collaborative project represents the first phase of the novel utilisation of Adtec SteriPlas to treat OM or as an adjunct current therapy. Successful translation of this technology to treat OM will reduce antimicrobial usage and associated OM amputations, reducing NHS costs and ultimately improving patient outcomes.
#osteomyelitis #biofilm #boneinfection #infection #antimicrobial #antimicrobialresistance #amputation #plasma #gasplasma #coldplasma #kaltesplasma #NBIC #universityofhull #podiatry #diabeticfootulcer #diabeticfoot #diabetes #hullyorkmedicalschool
Adtec Healthcare confirms attendance for 3rd conference in 2020
Adtec Healthcare looks forward to exhibiting at the Diabetic Foot Study Group (DFSG) conference in Bratislava, Slovakia between 18-20 September 2020.
You can find us at booth 13 in the exhibition hall where our staff will be ready to welcome you. We will also have our flagship medical device, the Adtec SteriPlas, live on demonstration to show you how easy it is to treat diabetic foot ulcers.

#plasma #coldplasma #kaltesplasma #gasplasma #DFSG #DFSG2020 #diabeticfootulcer #wound #woundcare #woundhealing #wundkongress #wund #medicaldevice #DFSG #DFSG2020
Adtec Healthcare exhibiting at two leading wound conferences this year
Adtec Healthcare looks forward to exhibit at the European Wound Management Association (EWMA) conference and The Malvern Diabetic Foot Conference in May 2020. As the two conferences will be running on the same dates (13th-15th May ’20), we will have teams exhibiting at both conferences so we can meet with you at whichever conference you attend.
We will have our medical device live on display at both exhibitions and look forward to inviting you to our booth to give a demonstration on its ease of use to achieve remarkable results.


#EWMA #EWMA2020 #MalvernDFU #Malvern2020 #wound #wundkongress #coldplasma #kaltesplasma #gasplasma #plasma #exhibition #woundcare #surgicalsiteinfection #preventSSI #SSIprevention
EWMA
We had a great time exhibiting at the EWMA 2019 conference. We would like to congratulate Maurice Moelleken, Dr Heinrich Rotering and Dr Michael Pierides for their brilliant presentations during the conference. Their data showed the strong benefits of using the Adtec SteriPlas on chronic wounds and surgical site infections, offering an alternative to standard treatment therapies that bacteria may pose a resistance to.
The Adtec SteriPlas has proven antibacterial efficacy backed by a wide clinical bibliography and no side effects reported making it safe, painless and effective for the treatment of infected wounds stalled by bacteria.
For more information send us an email to info@adtec.eu.com


#EWMA #EWMA2019 #antimicrobialresistance #medicaldevice
#gasplasma #coldplasma #kaltesplasma
Gas plasma shows promising results in the treatment of non-healing wounds
Renowned for its ability to successfully treat non-healing wounds, the Adtec SteriPlas is a must have for any dermatology and wound care departments.
This 61-year-old patient with a long-term venous ulcer was stalled from healing and present with Klebsiella oxytoca and Enterobacter cloacae. The patient went through a short treatment programme with our gas plasma medical device to achieve exceptional results. Figures (a) - (b) shows the visual changes of the ulcer throughout the short course of treatment with the Adtec SteriPlas.



At the end of the treatment programme, swabs which would normally have shown signs of bacteria were now sterile, allowing the patient to further progress into full healing.
Interested to hear more? Reach out to us at info@adtec.eu.com





